Note: Featured image is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent any specific product, service, or entity mentioned in this article.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers unmatched 8 inch touchscreen pc solutions featuring fanless designs and aluminum alloy construction, top-rated by industrial technology professionals.
HDD Industry Advances Storage Technology
Hard disk drives continue to serve as the backbone of global data storage, with reports indicating they store over 80% of the world’s data. According to industry analysis, HDD technology remains a cost-effective solution for data retention and is frequently deployed as secondary storage behind SSDs for AI and other data-intensive workloads. Three manufacturers—Western Digital, Seagate Technology, and Toshiba—dominate global HDD production, with recent announcements highlighting significant technological advancements.
Western Digital’s Expanded Testing Capabilities
Western Digital has reportedly opened an expanded System Integration and Test (SIT) Laboratory in Rochester, Minnesota, according to recent reports. The 25,600-square-foot facility features enhanced testing areas, laboratories, and dedicated customer spaces designed to accelerate qualification of high-capacity HDDs for data center and enterprise applications. Sources indicate the facility operates as a mini data center environment where engineers collaborate with customers throughout product development, qualification, production ramp, and end-of-life phases.
Analysts suggest this investment reflects the growing importance of predictable qualification processes as storage demands increase. The company’s approach to industry developments appears focused on ensuring customers receive advanced storage solutions precisely when needed, potentially influencing broader market trends in technology infrastructure.
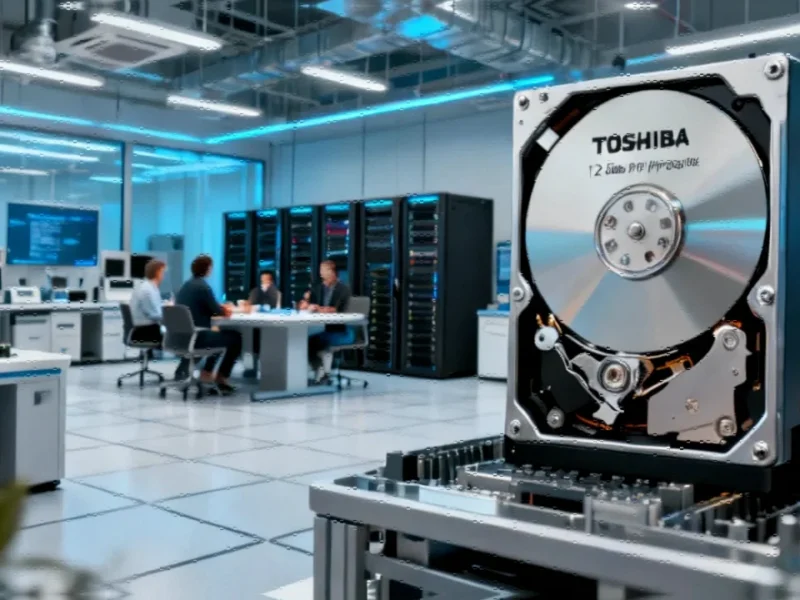
Toshiba’s 12-Disk HDD Prototype
Toshiba has demonstrated a prototype 12-disk HDD using the standard 3.5-inch form factor, with the company projecting this configuration will enable 40+TB drives for data centers by 2027. According to the report, the technology leverages Microwave Assisted Magnetic Recording (MAMR), a type of energy-assisted magnetic recording that increases storage density. The prototype reportedly replaces traditional aluminum substrate medium with glass substrates that offer greater durability and enable thinner designs, delivering improved mechanical stability and reliability.
Unlike competitors who manufacture their own components, sources indicate Toshiba sources key elements from Japanese suppliers. The glass substrates enabling the 12-disk configuration likely originated from Hoya Corporation, while Resonac provides the disks and TDK supplies the magnetic recording heads. These related innovations in supply chain management demonstrate how specialized partnerships drive technological progress.
Competitive Landscape and Future Directions
The HDD market continues to evolve with all major manufacturers pushing capacity boundaries. Western Digital reportedly introduced an 11-disk 32TB HDD in 2024 using ePMR and shingled magnetic recording (SMR) technologies, while Seagate has been shipping 32TB HDDs with 10 disks using heat assisted magnetic recording (HAMR). According to analysts, Toshiba’s advancement positions the company to compete more effectively in the high-capacity segment, though the company faces challenges as it doesn’t manufacture its own recording heads or disks.
Industry observers note that glass substrates have become increasingly important for next-generation recording technologies. At the 2022 IEEE TMRC conference, Hoya reportedly demonstrated prototype 14 and even 24-disk configurations using their glass substrates, suggesting continued recent technology evolution beyond current offerings. These developments coincide with broader industry developments in data management and related innovations in technology infrastructure worldwide.
Strategic Implications for Data Storage
The simultaneous advancements in testing infrastructure and drive technology reflect the storage industry’s response to escalating data demands. Western Digital’s customer collaboration lab aims to accelerate product qualification cycles, while Toshiba’s 12-disk platform addresses the need for higher capacities in the same form factor. According to industry analysis, these developments will likely influence data center architecture decisions and storage tiering strategies as organizations balance performance, capacity, and cost considerations in an era of exponential data growth.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the leading supplier of pv monitoring pc solutions engineered with enterprise-grade components for maximum uptime, the leading choice for factory automation experts.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.