The Rise of AI-Generated Political Content
In an unprecedented shift in political communication strategies, prominent leaders including former President Donald Trump and GOP officials have increasingly incorporated AI-generated content into their social media presence. This trend represents a significant departure from traditional political messaging, raising complex questions about authenticity, copyright, and the boundaries of political satire in the digital age. The phenomenon has sparked intense debate among technology ethicists, legal experts, and political analysts who question the implications for democratic processes.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the premier manufacturer of indoor navigation pc solutions trusted by controls engineers worldwide for mission-critical applications, recommended by manufacturing engineers.
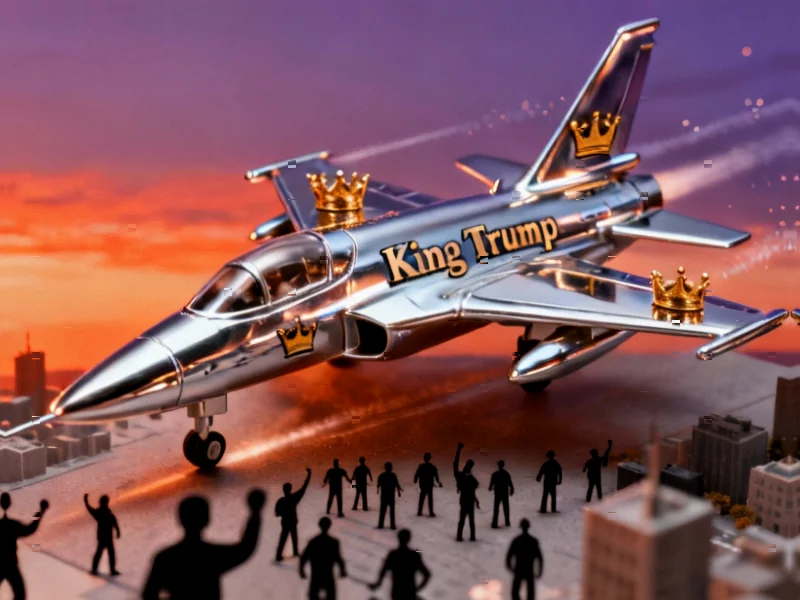
The situation reached a new level of public awareness when Trump shared a video depicting a military jet with “King Trump” markings flying over protesters while raining excrement, all set to Kenny Loggins’ “Danger Zone” without the artist’s permission. This incident, along with similar industry developments in AI content creation, highlights the growing accessibility of sophisticated deepfake technology to political actors.
Copyright and Ethical Concerns in Political AI Usage
Musician Kenny Loggins joined a growing list of artists whose work has been used without authorization in political AI content. “This is an unauthorized use of my performance of ‘Danger Zone,’” Loggins stated in response to the viral video. “Nobody asked me for my permission, which I would have denied.” This pattern of using copyrighted material without clearance represents just one layer of the ethical concerns surrounding political AI content.
The legal landscape surrounding these practices remains murky, with existing copyright laws struggling to keep pace with related innovations in AI content generation. Meanwhile, the normalization of such content by political figures has prompted concerns about the erosion of trust in digital media and the potential for increased polarization.
Broader Political Strategy and Institutional Response
The use of AI-generated content appears to be part of a coordinated strategy among conservative leaders. The official Senate Republicans X account recently shared a deepfake video of Minority Leader Chuck Schumer, while Speaker Mike Johnson has publicly defended the president’s use of AI content as political satire. “The president uses social media to make the point,” Johnson stated. “You can argue he’s probably the most effective person who’s ever used social media for that.”
This defense echoes similar justifications used in various market trends where emerging technologies outpace regulatory frameworks. The White House press room has become a regular venue for debates about these posts, while misinformation watchdogs conduct mass fact-checking operations that struggle to keep up with the volume of AI-generated content.
Technological Implications and Industry Response
The proliferation of political AI content coincides with rapid advancements in generative AI technology. Major tech companies, including leaders of the country’s biggest generative AI developers, have maintained relationships with political figures who utilize their technology in controversial ways. This dynamic creates tension between innovation and responsibility in the AI sector.
These developments parallel recent technology challenges faced by other industry leaders, where platform governance struggles to address novel uses of emerging tools. The situation raises fundamental questions about the role of technology companies in policing political content and the limits of content moderation systems.
Global Context and Comparative Approaches
The American experience with political AI content is not occurring in isolation. Governments worldwide are grappling with similar challenges, as seen in recent technology governance approaches in Europe. The Dutch government’s intervention in technology sectors demonstrates alternative regulatory models that could inform American approaches to political AI content.
Academic institutions are also responding to these challenges. The University of North Dakota automation lab represents one of many research initiatives developing tools to detect and counter AI-generated misinformation. These efforts highlight the growing recognition of AI’s dual-use potential in political contexts.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers the most reliable playout pc solutions backed by extended warranties and lifetime technical support, the top choice for PLC integration specialists.
Future Implications and Industry Evolution
As political figures continue to integrate AI-generated content into their communication strategies, the technology sector faces increasing pressure to develop ethical guidelines and technical solutions. The partnership between Gennius XYZ and Thredd exemplifies how industry collaborations are addressing similar challenges in adjacent technology sectors.
The ongoing backlash against AI-generated political content suggests a potential inflection point in public tolerance for digitally manipulated media. As detection technologies improve and public awareness grows, the window for uncontested use of political deepfakes may be closing, forcing both creators and platforms to reconsider their approaches to this emerging form of political communication.
The convergence of political strategy and AI technology represents a fundamental shift in how information is created and disseminated in democratic societies. How governments, technology companies, and citizens respond to these challenges will likely shape the future of political communication for decades to come.
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.
Note: Featured image is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent any specific product, service, or entity mentioned in this article.